






























PABLO LE (НИЖНИЕ КОНЕЧНОСТИ)
PABLO® Lower Extremity (Нижние конечности)
Всегда знает, куда движется терапия
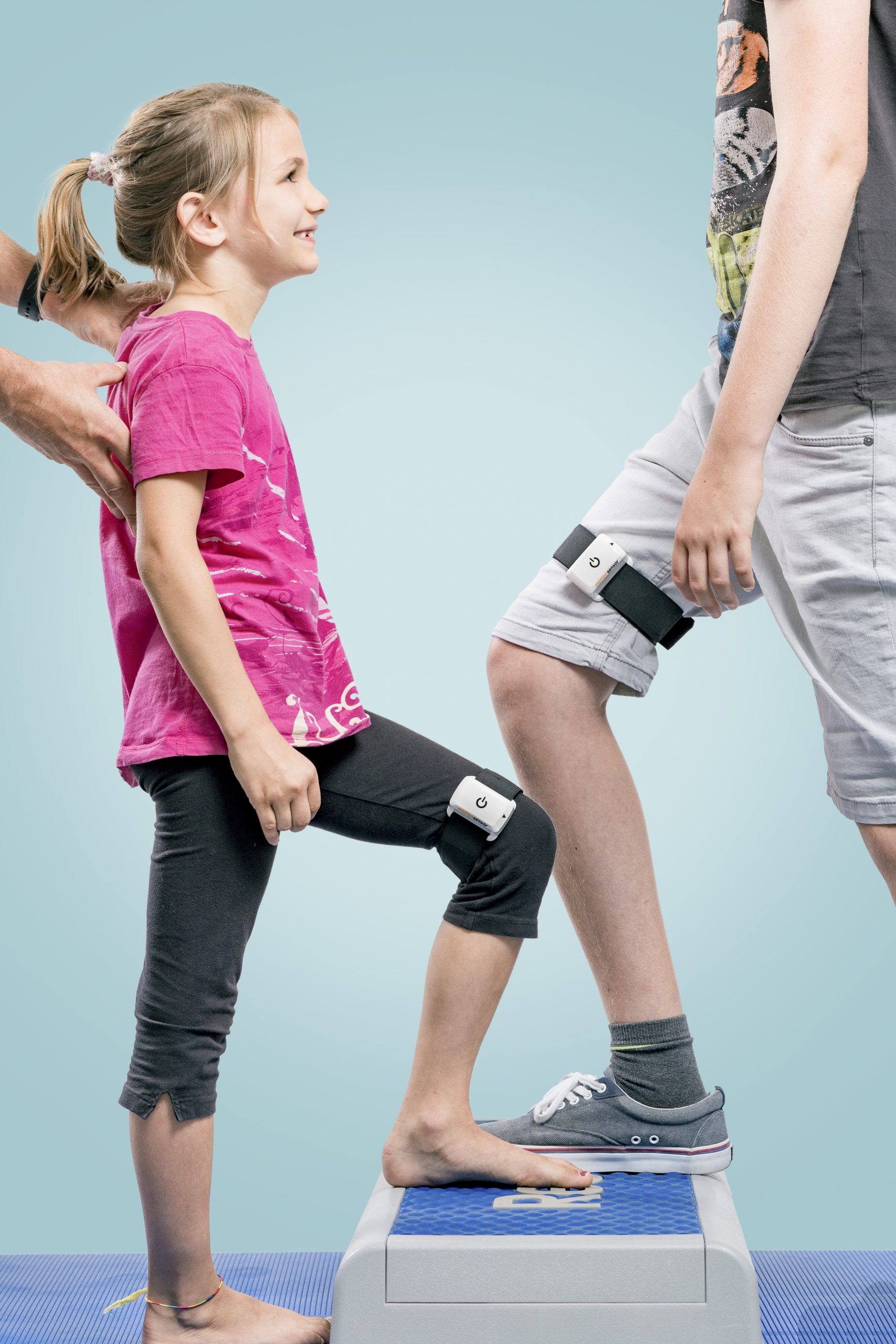
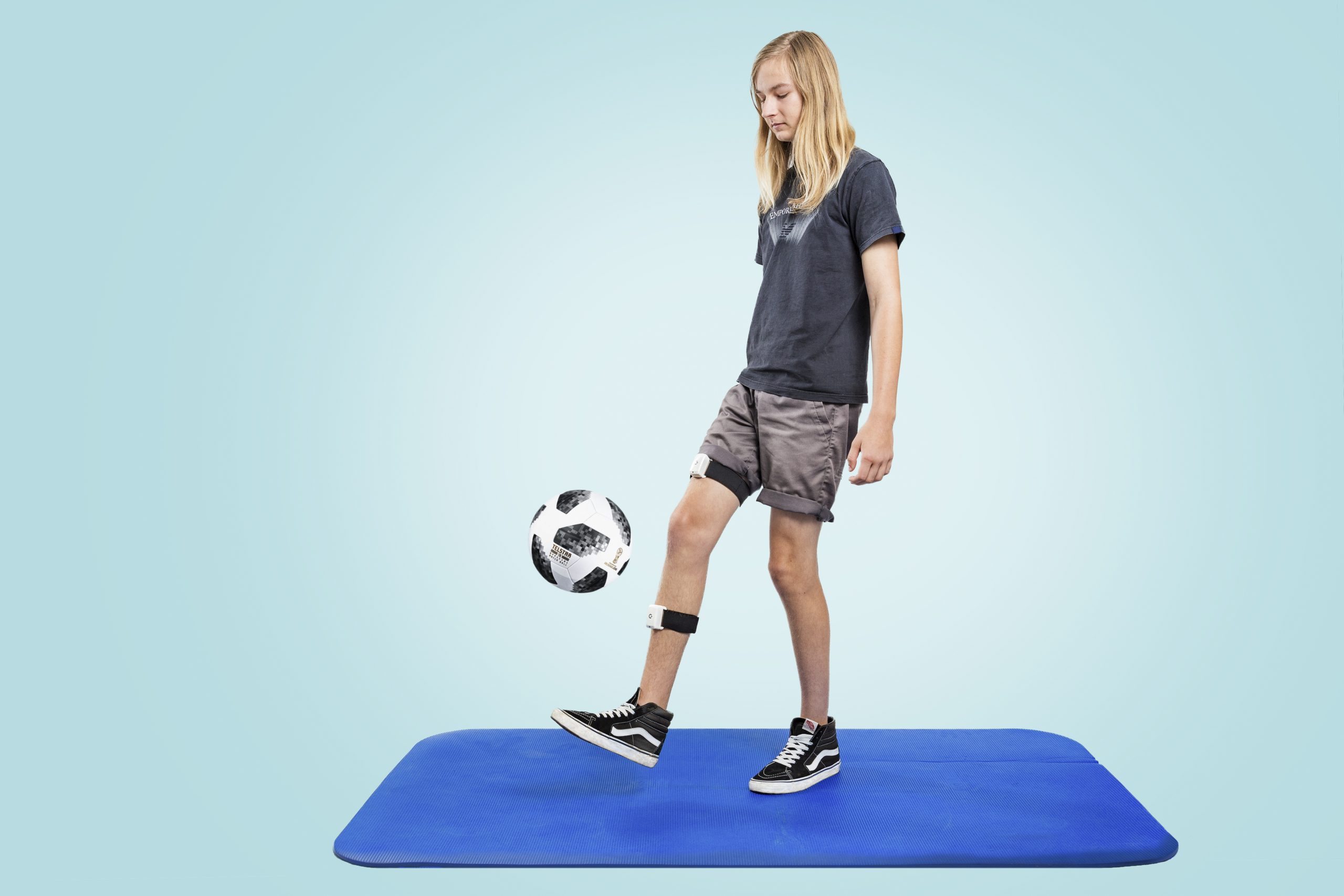
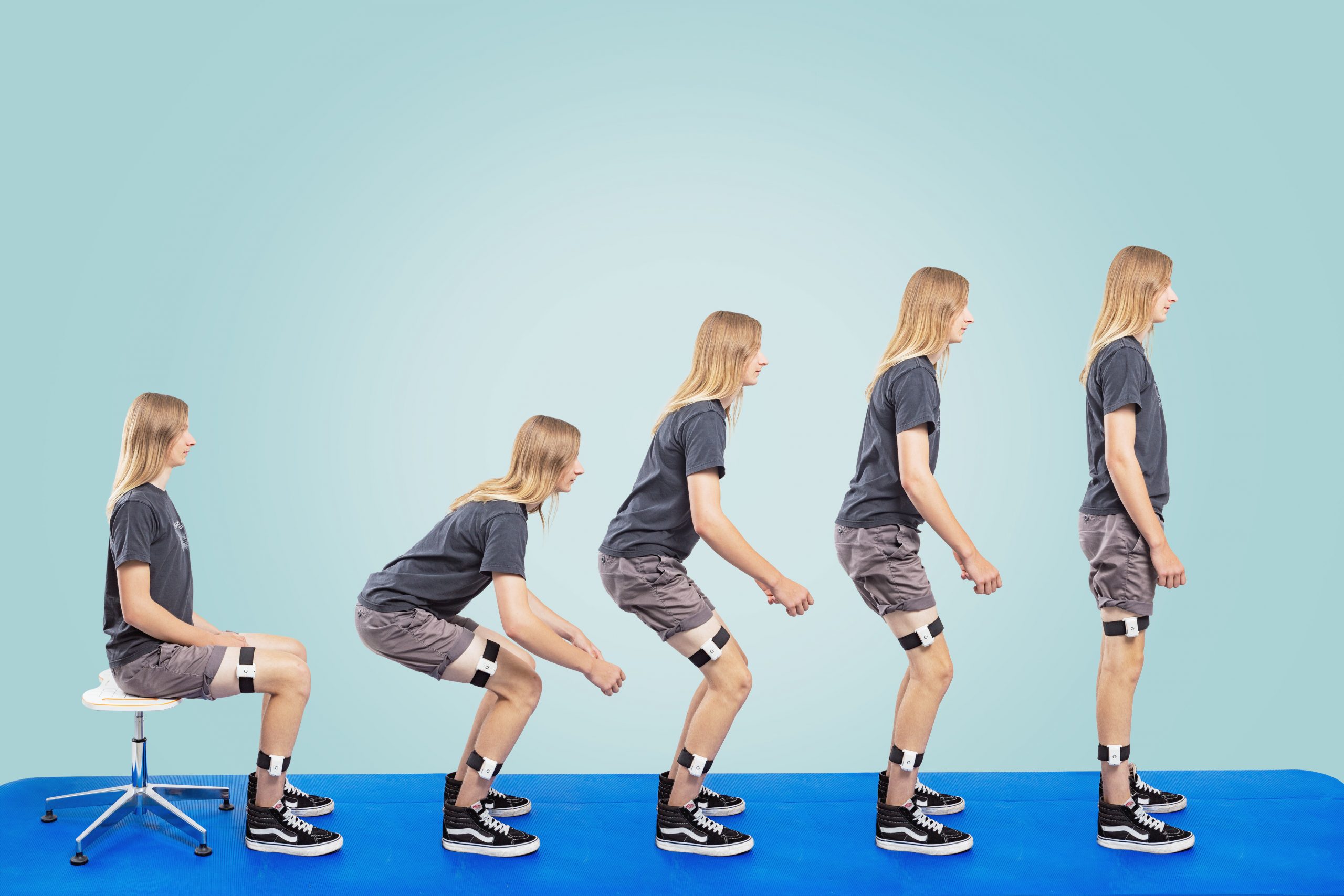
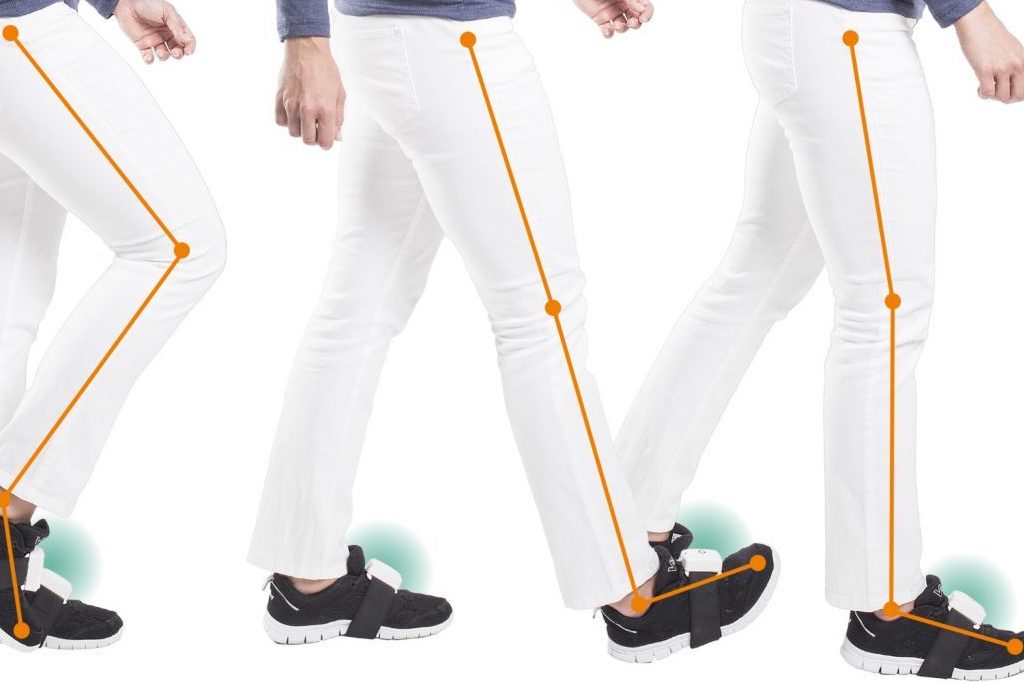
PABLO® Lower Extremity (Нижние конечности), система для анализа ходьбы и тренировки нижних конечностей, точно измеряет параметры, необходимые при выборе самого эффективного терапевтического подхода для восстановления ходьбы.
Простое и независимое от расположения, а также роста пациента применение, дополняет комплект.
Небольшое устройство, большой эффект.
Анализ ходьбы для:
- Оценки текущего состояния
- Отслеживание прогресса
- Оценки эффективности терапевтических подходов
- Оценки эффективности применяемых ортопедических/медицинских инструментов
- Обратной связи для пациентов (информация о текущем состоянии или прогрессе)
Для использования пациентами ортопедических, неврологических, педиатрических и гериатрических отделений.
Для применения в больницах, реабилитационных центрах, амбулаторных центрах, в практике частных физических терапевтов


- Простая интеграция в ежедневную практику:
- Адаптация уровня детализации оценок
- Стратегия терапии логично выстаивается из полученного анализа
- Простая настройка
- Может использоваться на всех типах покрытия
- Особенно важно при применении в гериатрии/неврологии без беговой дорожки
- Адаптируемое расстояние ходьбы
- Объективная оценка параметров патологической ходьбы / асимметрий в паттернах ходьбы
- Проведение анализа независимо от роста пациента
- Применение в педиатрии






- Инсульт
- Черепно-мозговая травма (ЧМТ)
- Травма спинного мозга (ТСМ)
- Опухоль головного мозга
- Болезнь Паркинсона
- Хронические состояния такие как рассеянный склероз
- Церебральный паралич
- Болезни моторных нейронов, например, амиотрофический боковой склероз (АБС)
- Мышечная дистрофия
- Паралич вследствие грыжи позвоночного диска
- Послеоперационная реабилитация, например, после эндопротезирования коленного или тазобедренного суставов (K-TEP, H-TEP), реконструкции передней крестовидной связки
- Переломы и травмы нижних конечностей (фаза реконструкции)
- Дегенеративные заболевания суставов (например, артроз)
- Ампутация
Потому что мы делаем только то, что научно обосновано.
2018
Jakob I, Kollreider A, Germanotta M, Benetti F, Cruciani A, Padua L, Aprile I.
PM&R, Volume 10, Issue 9, Supplement 2, S189-S197.
PubMed
2017
Bishop L, Gordon AM, Kim H.
American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. 2017 Jan;96(1):1-7.
PubMed
Jakob I, Kollreider A, Grieshofer P, Kreuzig W, Vursic M, Petzold G.
Neurologie & Rehabilitation Supplement 1; 2017
Hussain A, Balasubramanian S, Roach N, Klein J, Jarrasse N, Mace M, David A, Guy S, Burdet E.
Journal of Rehabilitation and Assistive Technologies Engineering. 2017 Vol 4: 1–16.
PDF (en)
Mace M, Hussain A, Diane Playford E, Ward N, Balasubramanian S, Burdet E.
V
IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics: [proceedings]. 2017:652-657.
PubMed
2016
Celadon N, Dosen S, Binder I, Ariano P, Farina D.
Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation. 2016 Aug 4;13(1):73.
PubMed, Pdf (en)
Orihuela-Espina F, Femat Roldán G, Sánchez-Villavicencio I, Palafox L, Leder R, Enrique Sucar L, Hernández-Franco J.
Journal of Hand Therapy. 2016 Jan-Mar; 29(1):51-7.
PubMed
2014
Gharabaghi A, Naros G, Khademi F, Jesser J, Spüler M, Walter A, Bogdan M, Rosenstiel W, Birbaumer N.
Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 2014 Dec; 8:429.
Eberhard Karls University Tuebingen, Germany. University of Leipzig, Germany. IRCCS, Venice, Italy.
Pdf (en), PubMed
Gharabaghi A, Kraus D, Leão MT, Spüler M, Walter A, Bogdan M, Rosenstiel W, Naros G, Ziemann U.
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 2014 Mar; 8:122.
Eberhard Karls University Tuebingen, Germany. University of Leipzig, Germany.
PubMed
Vukelić M, Bauer R, Naros G, Naros I, Braun C, Gharabaghi A.
Neuroimage. 2014 Feb; 87:147-53.
PubMed
Seitz RJ, Kammerzell A, Samartzi M, Jander S, Wojtecki L, Verschure P, Ram D.
Int J Neurorehabilitation 2014. 1:113.
Department of Neurology, University Hospital Düsseldorf, Germany. SPECS Lab, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, Spain. Tyromotion, Graz, Austria.
Open Access Research Article
Hartwig M.
Neurologie & Rehabilitation. 2014(2): 111-116.
Pdf (de), Pdf (en)
Sale P, Mazzoleni S, Lombardi V, Galafate D, Massimiani MP, Posteraro F, Damiani C, Franceschini M.
Int J Rehabil Res. 2014 Sep; 37(3):236-42.
Department of Neurorehabilitation, IRCCS San Raffaele Pisana. BioRobotics Institute, Scuola Superiore Sant‘ Anna, Polo Sant‘ Anna Valdera, Pontedera. Rehabilitation Bioengineering Laboratory. Neurological Rehabilitation Unit, Auxilium Vitae Rehabilitation Center, Volterra eSan Raffaele Portuense, Rome, Italy.
PubMed
2013
Glatz AH, Madle R, Sattler J.
Ergotherapie. 2013(4):25-29.
SeneCura Neurologisches Rehabilitationszentrum Kittsee, Österreich.
Pdf (de)
Brailescu CM, Scarlet RG, Nica AS, Lascar I.
Palestrica of third millennium – Civilization and Sport. Vol.14, no.4, October-December 2013, 263-270.
Carol Davila University of General Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania. National Institute for Rehabilitation, Physical Medicine and Balneology Bucharest, Romania. Floreasca Emergency Hospital, Bucharest, Romania.
Pdf
Pinter D, Pegritz S, Pargfrieder C, Reiter G, Wurm W, Gattringer T, Linderl-Madrutter R, Neuper C, Fazekas F, Grieshofer P, Enzinger C.
Top Stroke Rehabil. 2013 Jul-Aug; 20(4):308-316.
Departement of Neurology, Medical University of Graz, Austria. Division of Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology, Medical University Graz, Austria. Rehabilitation Clinic Judendorf-Strassengel, Austria.
PubMed
Borghese NA, Pirovano M, Lanzi PL, Wüest S, de Bruin ED.
Games for Health Journal: Research, Development, and Clinical Application. Volume 2, Number 2, 2013.
Department of Computer Science, University of Milan, Milan, Italy. Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria – Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy. Institute of Human Movement Sciences and Sport, Department of Health Sciences and Technology, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland.
Pdf, PubMed
Nica AS, Brailescu CM, Scarlet RG.
.
Stud Health Technol Inform. 2013:191:48-52.
National Institute for Rehabilitation, Physical Medicine and Balneology Bucharest, Romania. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department, Carol Davila University of General Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania.
PubMed, Pdf
Ortner R, Ram D, Kollreider A, Pitsch H, Wojtowicz J, Edlinger G.
15th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction 2013.
Pdf
2012
Sale P, Lombardi V, Franceschini M.
Stroke Res Treat. 2012:820931.
Department of Neurorehabilitation, IRCCS San Raffaele Pisana, Rome, Italy.
PubMed, Pdf
Hwang CH, Seong JW, Son DS.
Clin Rehabil. 2012 Aug; 26(8): 696–704.
From the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Republic of Korea.
PubMed
2011
Stein J, Bishop L, Gillen G, Helbok R.
Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011 Nov; 90(11):887-94.
Department of Rehabilitation and Regenerative Medicine, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York. Clinical Department of Neurology, Innsbruck Medical University, Innsbruck, Austria.
PubMed
Kaiser V, Kreilinger A, Müller-Putz GR, Neuper C.
Front Neurosci. 2011 Jul 5;5:86.
Laboratory of Brain-Computer Interfaces, Institute for Knowledge Discovery, Graz University of Technology, Austria. Department of Psychology, University of Graz, Austria.
PubMed, Pdf
Hartwig M.
Neurologie & Rehabilitation. 2011(1):42–46.
Pdf (de), Pdf (en)
Stein J, Bishop L, Gillen G, Helbok R.
IEEE Int Conf Rehabil Robot. 2011:5975426.
Department of Rehabilitation and Regenerative Medicine, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York. Clinical Department of Neurology, Innsbruck Medical University, Innsbruck, Austria.
PubMed
2010
Helbok R, Schoenherr G, Spiegel M, Sojer M, Brenneis C.
Clinical Department of Neurology, Neurological Intensive Care Unit, Medical University Innsbruck, Austria.
Mayr A, Kollreider A, Ram D, Saltuari L.
Hospital Hochzirl, Department of Neurology, Austria. Research Department for Neurorehabilitation, Bolzano, Italy. Tyromotion, Graz, Austria.










